Technology
MolYsis™ – Human DNA Depletion and Isolation of Pathogen DNA
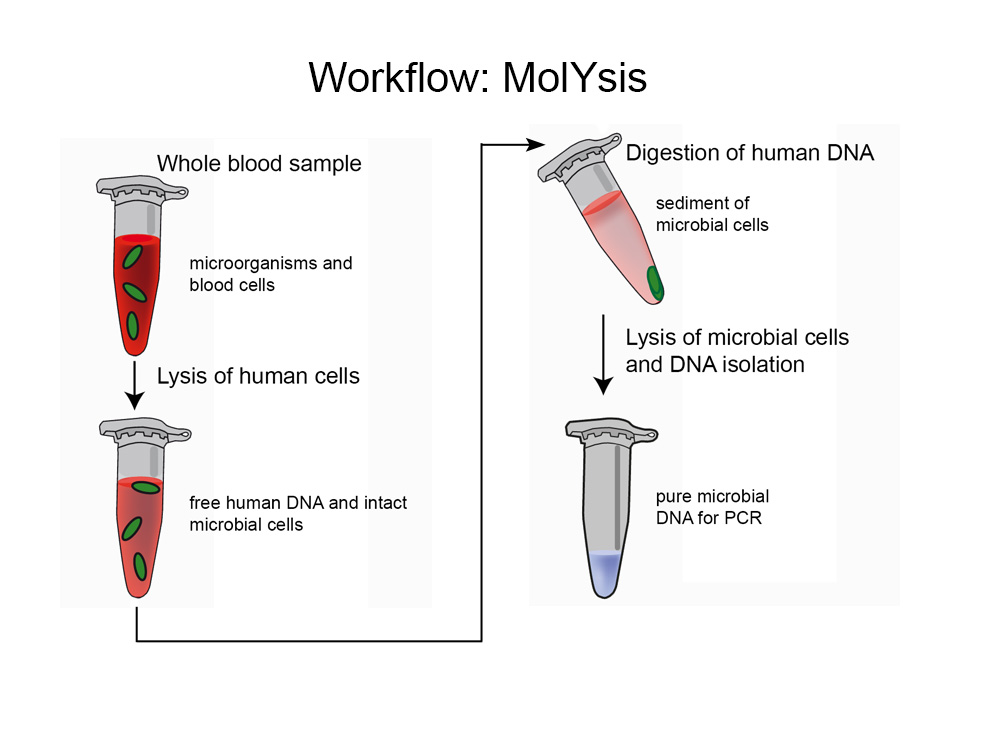 In clinical samples of infected patients, human DNA is in great excess to the microbial DNA which is the target of molecular analysis. PCR primers constructed to bind to microbial sequences tend to bind unspecifically to human sequences, thereby generating false positive results and reducing the sensitivity of the assay. This problem becomes particularly prominent in case of amplification assays targeting the ribosomal RNA genes like 16S and 18S of eubacteria and fungi, respectively.
In clinical samples of infected patients, human DNA is in great excess to the microbial DNA which is the target of molecular analysis. PCR primers constructed to bind to microbial sequences tend to bind unspecifically to human sequences, thereby generating false positive results and reducing the sensitivity of the assay. This problem becomes particularly prominent in case of amplification assays targeting the ribosomal RNA genes like 16S and 18S of eubacteria and fungi, respectively.
Molzym’s MolYsis™ technology greatly reduces the amount of host DNA. For this, samples like blood, other primary sterile body fluids and tissues are treated by a process involving the lysis of host cells and degradation of the released host DNA by a nuclease treatment. During this treatment microbial cells stay intact because of their rigid cell walls. In the following steps, the nuclease is inactivated and microorganisms are lysed enzymatically. The DNA is finally purified and isolated by a bind-wash-elute process. Notably, free floating DNA from dead microorganisms is also degraded such that amplicons in PCR analysis come only from intact, living microorganisms.
Broad-Range Detection of Pathogen DNA
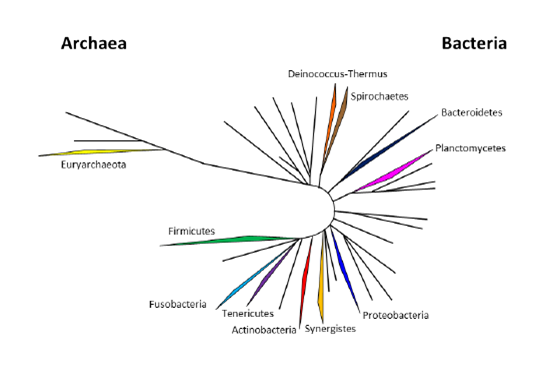
Identification by Sequencing Analysis
 The precise identification of pathogens is performed by Sanger sequencing analysis. For this purpose, amplicons are purified and sequenced using the primers supplied with the kit. The sequences are then pasted into the freely available online BLAST tool (www.sepsitest-blast.com). This tool contains quality-edited, full length sequences of the 16S rRNA gene of 7,042 cultivated bacteria and the 18S rRNA gene of 342 selected cultivated members of the genera Candida, Aspergillus and Cryptococcus. The data output of the search will result in the designation of the species with highest sequence identity score.
The precise identification of pathogens is performed by Sanger sequencing analysis. For this purpose, amplicons are purified and sequenced using the primers supplied with the kit. The sequences are then pasted into the freely available online BLAST tool (www.sepsitest-blast.com). This tool contains quality-edited, full length sequences of the 16S rRNA gene of 7,042 cultivated bacteria and the 18S rRNA gene of 342 selected cultivated members of the genera Candida, Aspergillus and Cryptococcus. The data output of the search will result in the designation of the species with highest sequence identity score.
Assays are Contamination-Free
 Generally, pathogens are present at low loads in clinical samples. Consequently, amplification needs extended cycling in order to detect target amounts in the range of femtograms to picograms per assay. This raises the possibility of amplification of irrelevant microbial DNA contaminating assay reagents. Molzym solves this problem by providing ultra-clean master mixes with their kits. Molzym has developed a technology of manufacturing assay reagents that are highly active over 40 cycles of PCR amplification without amplicons showing up from traces of contaminating DNA (false positive rate at <5%).
Generally, pathogens are present at low loads in clinical samples. Consequently, amplification needs extended cycling in order to detect target amounts in the range of femtograms to picograms per assay. This raises the possibility of amplification of irrelevant microbial DNA contaminating assay reagents. Molzym solves this problem by providing ultra-clean master mixes with their kits. Molzym has developed a technology of manufacturing assay reagents that are highly active over 40 cycles of PCR amplification without amplicons showing up from traces of contaminating DNA (false positive rate at <5%).
Automation in DNA Extraction
 Molzym’s most recent development is the automation of the MolYsis™ process of host DNA depletion and isolation of enriched pathogen DNA from a variety of fluid and tissue specimens. The completely automated process is operated on the SelectNA™plus instrument using the buffers and reagents supplied with the Micro-Dx™ kit.
Molzym’s most recent development is the automation of the MolYsis™ process of host DNA depletion and isolation of enriched pathogen DNA from a variety of fluid and tissue specimens. The completely automated process is operated on the SelectNA™plus instrument using the buffers and reagents supplied with the Micro-Dx™ kit.Routine Validation
Please inquire for more information on Molzym’s products, applications and clinical performances at Diese E-Mail-Adresse ist vor Spambots geschützt! Zur Anzeige muss JavaScript eingeschaltet sein! or call at +49 (0) 421 / 69 61 62 0.
